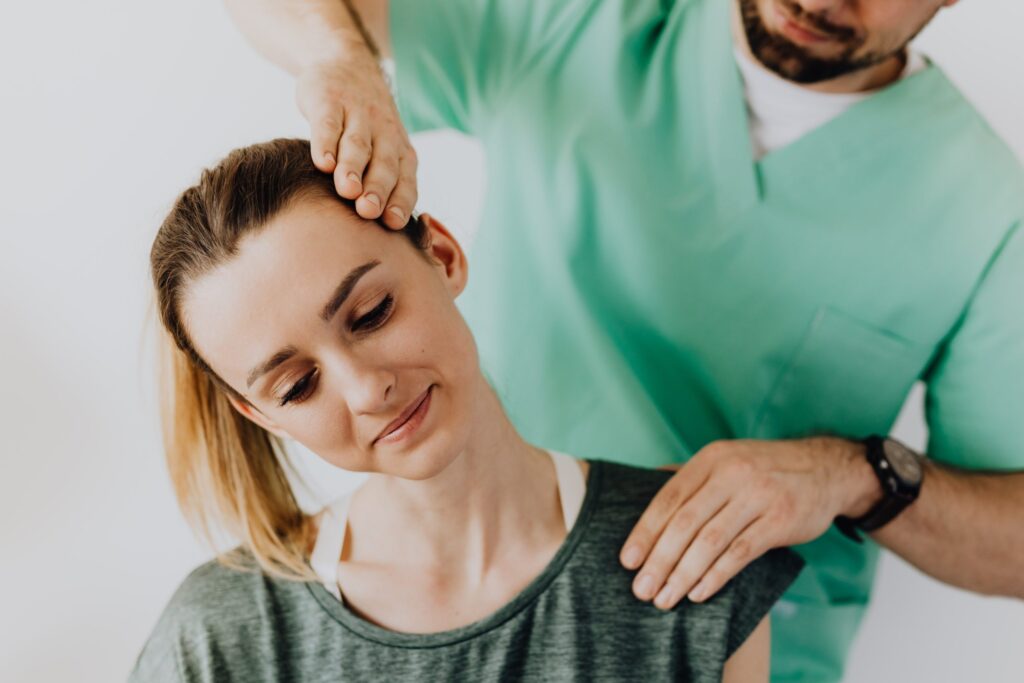
Neck pain is pain felt in the back of the neck – the upper spine area, just below the head. When certain nerves are affected, the pain can extend beyond the back of the neck to areas such as the upper back, shoulder, and arm. It is estimated that neck pain affects approximately 30% of the US population each year. Neck pain can be caused by sudden trauma such as a fall, sports injury, or car accident, or by long-term problems in the spine.
People with neck pain can have difficulty performing activities such as working, driving, playing sports, or simply turning their heads. The majority of neck pain episodes do not require surgery and respond best to physical therapy. Physical therapists design individualized treatment programs to help people with neck pain reduce or eliminate pain, regain normal movement, and get back to their regular activities.
How Are you It Feel?
People with neck pain may experience stiffness in the neck, and may describe the pain they feel as:
- Sharp
- Stabbing
- Dull
- Aching
- Throbbing
- Tingling
Neck pain caused by irritated nerves may extend into the upper back, shoulder blades, shoulders, arms, or hands. This condition is called “radiculopathy.” Your physical therapist can help determine if this condition is occurring and will work closely with your physician and surgeon to determine the correct treatment.
Signs and Symptoms
The type and location of your symptoms depend on the tissue or structure that is affected, and the severity of the injury. Neck pain can cause any of the following signs:
- Inability to bend or rotate the neck
- Difficulty looking up
- Difficulty looking over the shoulder
- Weak arm and shoulder muscles
- Muscle spasms
Neck pain can cause any of the following symptoms:
- Pain in the neck, upper back, shoulders, arms, or hands
- Numbness or tingling in the neck, shoulders, arms, or hands
- Weakness in the arms
- Increased pain when coughing, sneezing, reaching, or sitting
- Inability to stand straight or sit up straight
- Stiffness when trying to move, or a feeling of being “stuck” in a position such as stooped forward, or with the head leaning to the side
- Tight muscles
- Headaches
- Inability to remain in one position for a long period of time, such as sitting or standing, due to pain
- Pain that is worse in the morning or at night
- Difficulty sleeping due to pain
How Is It Diagnosed?
Your physical therapist will conduct a thorough examination that includes taking your health history. He or she will also ask you detailed questions about your pain or injury, such as:
- How and when did the pain start?
- What type of discomfort do you feel, and where do you feel it?
- At what time of day is it worse?
- What can’t you do right now in your daily life due to the pain?
Your physical therapist will perform tests on your body to find physical problems, such as:
- Difficulty moving
- Weakness or tightness in the muscles
- Loss of skin sensation (numbness) in some areas
- Loss of reflexes
- Joint stiffness
- Poor posture
- Difficulty walking
If your physical therapist finds any of the above problems, physical therapy treatment may begin right away to help get you on the road to recovery and back to your normal activities.
We are here for you.
Our therapists can help resolve your pain and teach you how to prevent it from recurring: https://apexnetworkpt.com/request-an-appointment/